Bookkeeping
The Value of the Online Accounting MBA Southeastern

Both total assets and total liabilities will be listed on the balance sheet. Understanding these acronyms is essential to navigating the accounting/finance world. With this knowledge, you’ll be able to analyze financial statements more effectively, assess a company’s performance, and make informed decisions.
Financial accounting
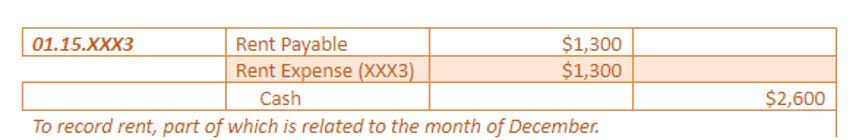
Rasmussen University may not prepare students for all positions featured within this content. Rasmussen University is accredited by the Higher Learning Commission, an institutional accreditation agency recognized by the U.S. By studying the definition alone, we learned some important concepts in petty cash accounting. The amounts, figures, and other data in the financial reports have meanings that are useful to the users. Using one of the examples above, it is not enough to record that the company paid salaries for April. It must include monetary figures – say for example, $20,000 salaries expense.
Operating Expenses (OPEX)

Current liabilities are debts that are paid in 12 months or less, and consist mainly of monthly operating debts. Examples of current liabilities may include accounts payable and customer deposits. Current assets are items that are completely consumed, sold, or converted into cash in 12 months or less. Examples of current assets include accounts receivable and prepaid expenses.
- Assessing a company’s valuation frequently brings up ‘Book Value Per Share’, revealing the amount shareholders would theoretically receive if all assets liquidated/debts were repaid today itself.
- Primarily, it’s an indication of a company’s net worth, revealing the amount that would be returned to shareholders if all its assets were liquidated and all its debts paid off.
- It will result in an increase in the company’s inventory which is an asset while reducing cash capital which is another asset if a business buys raw materials and pays in cash.
- These abbreviations encapsulate complex concepts in short, memorable forms and are essential for anyone involved in accounting or finance.
- Alternative Investment Management (AIM) involves managing investments in asset classes other than stocks, bonds, and cash-like private equity.
- As a business owner, you’ll make at least one annual payment to the IRS, although some businesses are required to pay quarterly or monthly taxes.
IFRS – International Financial Reporting Standards
As you can see, owner or shareholder equity is what is left over when the value of a company’s total liabilities are subtracted from the value of its assets. To become a public accountant, you’ll typically need to become a https://bluetvbrasil.com.br/church-accounting-payroll-and-cfo-services/ CPA and have a four-year degree in accounting from an accredited college or university. In addition to passing the CPA exam, public accountants must also meet continuing education requirements set by state boards of accountancy. Typically, management accountants have at least a bachelor’s degree in accounting or a related field.

CECL – Current Expected Credit Loss

Smart investors don’t only look at today’s stock se in accounting price or short-term market trends. Shareholders’ equity is an important aspect in a company’s financial reports that show its actual value. This helps investors decide whether to buy, sell, or hold onto a stock for the long term, looking beyond immediate market changes.

The four primary FS are the balance sheet, income statement, cash flow statement, and statement of shareholders’ equity. On the Balance Sheet, stockholders’ equity is presented as a major section, typically after assets and liabilities. It details the total amount of equity and often breaks down the primary components such as common stock, additional paid-in capital, and retained earnings. This presentation aligns with the accounting equation, showing how assets are financed by either liabilities or owners’ equity. Stockholders’ equity is composed of several accounts that detail the sources of ownership capital. The main elements typically include common stock, preferred stock, additional paid-in capital, retained earnings, treasury stock, and accumulated other comprehensive income or loss.
